Keramische Gasentladungsröhre
Keramische Gasentladungsröhre is the most widely used switching device in lightning protection equipment. Gas discharge tube (GDT) uses metallized ceramic tubes and two or more electrodes to seal one or more discharge gaps. Inert gas is filled inside the ceramic gas discharge tube, and active electron powder is coated on the effective electron emission surface of the electrodes. The distance between electrodes less than 1mm can ensure the stability of the breakdown voltage of the discharge tube. The ceramic gas discharge tube is cylindrical in shape and has two structural forms with and without leads. Keramische Gasentladungsröhres are used in communication or signal circuits with AC not exceeding 1200V and DC not exceeding 1500V, especially in the protection of information and signal systems. The tube is filled with an inert gas with stable electrical properties, such as argon and neon.
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt die Schaltsymbole der Gasentladungsröhre unter verschiedenen Bedingungen.
Wenn die Spannung an der Gasentladungsröhre ihre Entladungsgleichspannung erreicht, zerfällt das interne Gas und entlädt sich. Die Volt-Ampere-Kennlinie der Gasentladungsröhre ist nichtlinear und der Durchschlagsprozess ist in drei Stufen unterteilt: Der Gleichstromwiderstand bleibt vor dem Durchschlag über 10 °Ω; Im Moment des Durchbruchs fallen die Impedanz und der Röhrenspannungsabfall stark ab und der Leitungsstrom steigt stark an. Der Impedanz- und Röhrenspannungsabfall bleibt unmittelbar nach dem Durchschlag auf einem sehr niedrigen Niveau und setzt sich fort, bis die Spannung auf der Leitung niedriger als die Lichtbogenspannung der Gasentladungsröhre ist, und kehrt dann von selbst in den Zustand des offenen Stromkreises zurück.
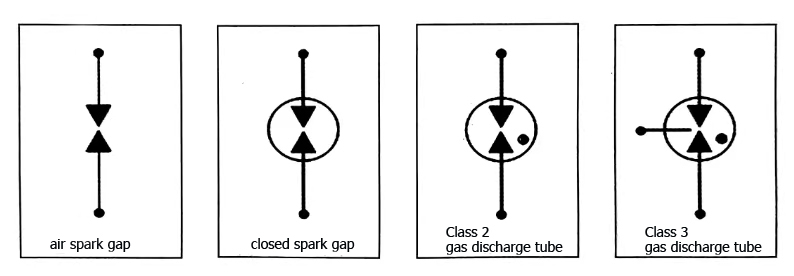
Symbol für den Stromkreis der Gasentladungsröhre
